|
BIOENERGY Corporation
|
Making food waste into energy
Traditionally, food waste was incinerated and not recycled due to difficulty in separation. It is now generated into biogas fuel using a methane fermentation system. The resulting fuel is used in two gas engines to generate approximately 24,000 kWh of electricity per day, equivalent to the power consumption of some 2,400 households. Since it is generated from biomass, this electric power is regarded as natural energy and recognized as green power.
Surplus biogas is also refined and supplied to the public. Generation of electric power and gas from food waste helps to slow global warming, and has an effect of cutting carbon dioxide emissions by about 6,380 tons/year.
Receiving poorly separated food waste
The BIOENERGY Corporation performs pulverization and sorting of poorly separated food waste to remove substances unsuited to fermentation. Therefore, complete separation is not required. Accumulated food waste does not need to be kept under cool conditions given that the process can be performed irrespective of the quality of the waste. Accumulated food waste does not need to be kept under cool conditions given that the process can be performed irrespective of the quality of the waste.
 |
|||
| I: Standard form of food waste (in a packed state) II: Example of well-sorted waste (food waste after cooking) III: Acceptable though not desirable (mixed with disposable chopsticks, plates, spoons) IV: Example of unacceptable waste (containing scant food waste) *As a rough guideline for separation, food waste is recyclable if the content of substances unsuited to fermentation does not exceed around 10%. *Any food waste containing a high percentage of unsuitable substances may be accepted though a different unit price of acceptance applies. |
|||
Treatment process
Food waste collected and transported from across the capital region is received at any time on any day, except for several days designated each year for regular inspections. It is processed into fine pieces using a powerful pulverizing machine. A sorting machine then removes plastic waste and other components unsuited to fermentation. Food waste used as a material for methane fermentation is stored and methane fermentation is implemented. The resulting biogas is used in gas engines to produce electric power and heat energy. The generated biogas is also supplied as gas after it is collectively confirmed with Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. that it is possible to do so. Half the 24,000 kWh of power generated each day is sold to electric power companies, while the remainder is consumed for operation of BIOENERGY facilities.
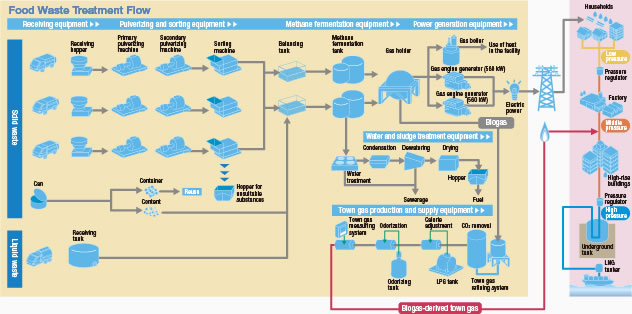
Methane fermentation technology
This technology takes advantage of microbial activity that typically occurs anywhere in nature to decompose organic food waste and generate flammable methane gas. It has been in practical use for over 100 years. Methane fermentation, also known as anaerobic digestion, occurs under air-free conditions. We may sometimes see bubbles rise in lakes, ponds and rivers; these contain high concentrations of methane gas. Methane fermentation technology is an exact application of this methane generation process.
Food waste contains numerous combustible substances, but it is so high in moisture content that it is difficult to effectively recover its energy by means of simple combustion. Methane fermentation facilitates recovery of energy contained within it in the form of biogas.